 Renesas Electronics today announced a joint development of the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator virtual platform (VP) for Renesas’ R-Car V3M, an automotive system-on-chip (SoC) for advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS) and in-vehicle infotainment systems. The VP simulates image recognition and cognitive intellectual properties (IPs) in the R-Car V3M SoC and realizes embedded software development using a PC only, which enables the VP to shorten development time as well as improve software quality. The VLAB/IMP-TASimulator is one of the latest software development tools for the Renesas R-Car V3M and is part of Renesas autonomy™ concept, which was announced in April 2017.
Renesas Electronics today announced a joint development of the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator virtual platform (VP) for Renesas’ R-Car V3M, an automotive system-on-chip (SoC) for advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS) and in-vehicle infotainment systems. The VP simulates image recognition and cognitive intellectual properties (IPs) in the R-Car V3M SoC and realizes embedded software development using a PC only, which enables the VP to shorten development time as well as improve software quality. The VLAB/IMP-TASimulator is one of the latest software development tools for the Renesas R-Car V3M and is part of Renesas autonomy™ concept, which was announced in April 2017.
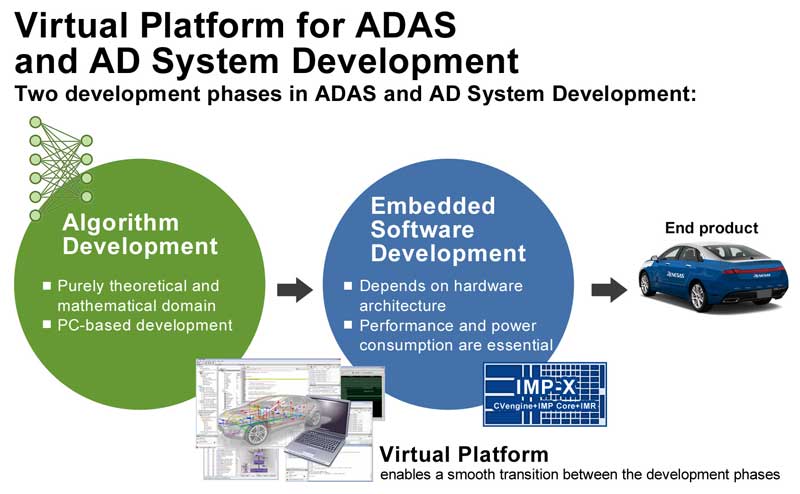
In ADAS and automated driving systems, algorithm development, including object detection and recognition to estimate the position of the vehicle, has become more complex and larger scaled, and algorithm development by PC has become the standard. However, it is difficult to port PC-developed algorithms to embedded software that deeply depends on hardware architecture. This makes it essential to have a development environment that enables a smooth transition or integration between the algorithm development phase and the embedded software development phase.
 To address this need, Renesas and ASTC have jointly developed the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator VP, which enables embedded software development for the R-Car V3M using the PC only. ASTC’s core technology, VLAB, simulates target hardware on the PC to enable system developers to develop embedded software only with a PC, eliminating the use of actual hardware. This enables system developers to check and control the hardware on a virtual environment displayed on the PC. In addition, the VP can efficiently detect defects in the developed software. By using the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator, system developers can develop high-quality software in less than half the development time.
To address this need, Renesas and ASTC have jointly developed the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator VP, which enables embedded software development for the R-Car V3M using the PC only. ASTC’s core technology, VLAB, simulates target hardware on the PC to enable system developers to develop embedded software only with a PC, eliminating the use of actual hardware. This enables system developers to check and control the hardware on a virtual environment displayed on the PC. In addition, the VP can efficiently detect defects in the developed software. By using the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator, system developers can develop high-quality software in less than half the development time.
Key features of the VLAB/IMP-TASimulator
- Significant reduction in software development period by reproducing R-Car V3M’s IMP-X5 image recognition engine on PC
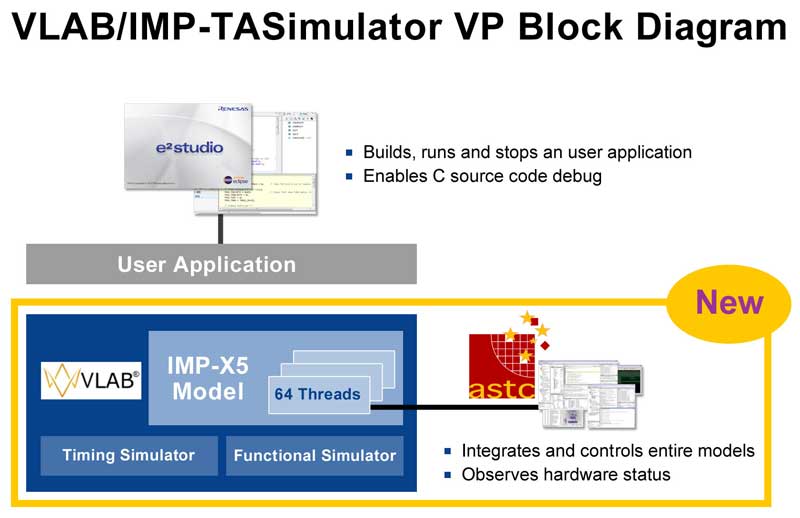
The new VP reproduces the IMP-X5’s built-in 64 thread MIMD processor on the PC, which enables debugging such as step execution, break, and variable reference of software written in C language dedicated to multithreaded programming. This reduces the software development period dramatically compared to when not using this virtual environment. - ASTC’s timing-correlated simulation technology enables an accurate estimation of the hardware processing time
The new VP includes a timing-correlated simulator that accurately grasps and reflects the hardware key timing and efficiently simulates the IMP-X5 by modeling the complicated timing behaviour of the cache, bus, processor and other major components. This allows system developers to estimate the hardware processing time at least 100 times faster than the currently used cycle-based simulator.
ASTC (Australian Semiconductor Technology Company), along with its subsidiary VLAB Works, delivers a wide range of tools, IP, and design services, into the embedded semiconductor, software, and systems design markets.
www.astc-design.com
www.vlabworks.com
Renesas Electronics Europe | www.renesas.com


