There has been an explosion in the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in the last decade, in markets ranging from medical devices to home and building automation to industrial automation. These are devices such as wearables, sensors, appliances and medical monitors – all connected, collecting and sharing massive amounts of data. A new forecast from International Data Corporation (IDC) estimates that there will be 41.6 billion connected IoT devices, or “things,” generating 79.4 zettabytes (ZB) of data in 2025.
A key driver for this explosion in IoT is ubiquitous wireless connectivity that allows things to be connected to each other and to the internet. This hyper-connectivity has a lot of advantages such as automated control, easy communication between devices and sharing of data. It also allows collection and sharing of massive amounts of data that can be harvested and used to make intelligent decisions. As the number of connected devices grows, so does the amount of data that is generated. IDC forecasts that the amount of data generated by these devices will see a compound annual growth rate of 28.7% over the 2018-2025 forecast period.
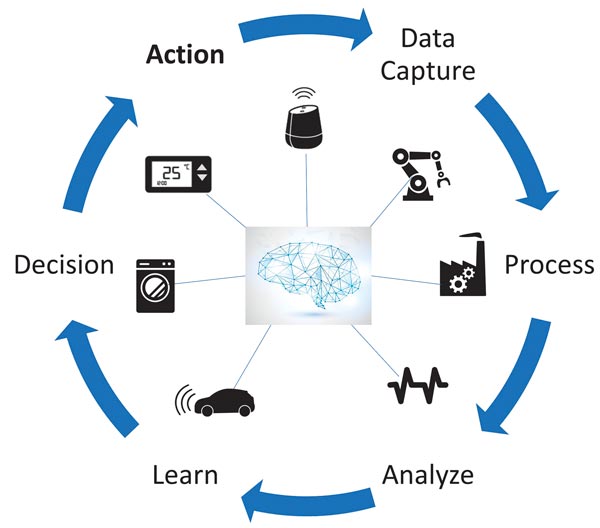
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the next logical step in making IoT even more useful. Intelligence can be built into IoT end devices to enable them to not only collect and share data but also to analyze it, learn from it and make decisions and act on it, without any human intervention. A combination of AI and IoT (AIoT) creates “intelligent” devices that learn from the generated data and use these insights to make autonomous decisions. New AI technologies are enabling intelligence on the edge and are significantly reducing the need for, and costs associated with cloud analytics. AI is expected to be the technology that helps IoT reach its fullest potential.
AIoT allows computation to move closer to the data. AI technologies, running on edge devices, can automatically process and analyze data generated by sensors and other IoT devices – such as temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration or sound – and use this information to make decisions and trigger actions.
Why AI at the edge?
In the past, AI applications have mainly run in the cloud due to complexity of the machine learning models. However, there are some applications that cannot run in the cloud due to lack of reliable and high bandwidth connectivity or when the application is such that it needs the models to be run at the device itself. These could be applications that need fast, real-time operation, which precludes the use of the cloud due to its latency. Examples of such applications are virtual assistants, industrial control, face recognition or medical devices that need quick real-time responses and cannot tolerate the latency of the cloud connection. Additionally, there might be concerns about security and privacy of data, driving the need to store and process data on the local device. Cloud connectivity and services can also be expensive and can drive up the cost of the devices or services associated with its use.
AI at the edge, therefore, provides advantages of autonomy, lower latency, lower power, lower requirement for bandwidth, lower costs and higher security, which make it more attractive for new emerging applications and use cases. Increased compute capability on the edge devices enables AI capability. AI finds use in many IoT applications such as vibration analysis, voice processing, image classification and computer vision, which need a combination of DSP compute capability and inference using machine learning.
AI in IoT – Market Drivers and Trends
AIoT allows users to convert raw IoT data into useful insights that the system can learn from and that can drive decision making. MarketsandMarkets forecasts that the global AI in IoT market size will grow from USD 5.1 billion in 2019 to USD 16.2 billion by 2024, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 26.0% during the forecast period. According to MarketsandMarkets, the major factors expected to drive the market are the need to efficiently process huge volumes of real-time data being generated from IoT devices to gain valuable insights, real-time monitoring, enhanced user experience and reduced maintenance cost and downtime.
Key trends in the market:
- The AI-enabled edge device market will be the fastest-growing segment within the AIoT
- There is growing adoption of AI technologies in IoT end devices and companies are moving from cloud-based AI to edge AI to reduce latency and cost and enable real-time monitoring.
- An analysis from Deloitte predicts sales of edge AI chips to exceed 1.5 billion units, representing annual unit sales growth of at least 20%.
- Gartner predicts that by 2022, more than 80 percent of enterprise IoT projects will include an AI component, up from only 10 percent today
- A lot of technology companies in the IoT space are investing significantly in AI in order to deliver new “intelligent” products, increase business efficiency and use data to drive business insights and enhance customer experience.
- Venture capital funding and acquisitions of AI-focused IoT start-ups is growing fast.
- Vendors of IoT platforms such as Amazon, IBM, Microsoft and Oracle, are integrating AI capabilities on their major general-purpose and industrial IoT platforms.
Advantages of AIoT
AI in IoT offers a whole slew of benefits to users and organizations such as true intelligent automation, a richer user experience, deeper business insights and operational efficiencies. Here are a few of these benefits:
Increased operational efficiency
AIoT can process and detect patterns in real-time operational data that are not visible to the human eye and can use that data to set operating conditions in real-time, that result in optimal business outcomes. AI can thus help to optimize production processes and improve workflow resulting in increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Improved risk management
AI can help institutions to use data to identify risks in a timely manner and use these insights to optimize their processes to increase safety and reduce loss and make better informed business decisions. Applications where AI can help to reduce risk include predicting mechanical faults on airlines and detecting safety risks on a factory floor.
New products and services
AI and the ability to process and draw insights from large amounts of data, has opened up new technologies that did not previously exist such as voice recognition, face recognition and predictive analysis. These newly created capabilities can be used in many applications such as use of robots in delivery services or for disaster search and rescue operations, smart video doorbells, voice based virtual assistants and predictive maintenance for vehicles or building automation systems, amongst others.
Reduced unplanned downtime
In manufacturing, unplanned downtime of machinery resulting from equipment breakdown can be very disruptive to business. Predictive maintenance can help in predicting equipment failure by analyzing data from machinery and scheduling maintenance proactively, resulting in reduced incidence and costs of unplanned downtime.
Improved customer experience
In the retail environment, AIoT helps to tailor the shopping experience and provide personalized recommendations based on customer intelligence, demographic information and customer behavior.
Reduced costs of products
By bringing analysis and decision making to the edge, AI helps to reduce volume of data that needs to be transferred to the cloud and hence reduce costs related to cloud connectivity and services.
Applications
 AIoT enables new and advanced level of solutions that can transform businesses, enrich the user experience and increase safety and security. Here are some applications that benefit from AI:
AIoT enables new and advanced level of solutions that can transform businesses, enrich the user experience and increase safety and security. Here are some applications that benefit from AI:
Agricultural AIoT
 Agriculture is one of the key segments that can benefit from AIoT. AI is used to create an intelligent system that adjusts parameters based on weather conditions, water usage, temperature and crop/soil conditions. The data from sensors is analyzed to make optimal decisions on crop choices, fertilizers, irrigation and pest control. AI helps farmers in enhancing their yields, do seasonal forecasting and weather prediction for crop planning and utilizing resources in the most optimal way. Computer vision with AI is used to monitor crops and large farmlands to identify problem areas and generate alerts when needed.
Agriculture is one of the key segments that can benefit from AIoT. AI is used to create an intelligent system that adjusts parameters based on weather conditions, water usage, temperature and crop/soil conditions. The data from sensors is analyzed to make optimal decisions on crop choices, fertilizers, irrigation and pest control. AI helps farmers in enhancing their yields, do seasonal forecasting and weather prediction for crop planning and utilizing resources in the most optimal way. Computer vision with AI is used to monitor crops and large farmlands to identify problem areas and generate alerts when needed.
Robots
Robots, in manufacturing as well as consumer products, are examples of applications that are very well suited for AI. Robotic vacuum cleaners have sensors that gather data on the environment and use AI to make decisions on how to traverse a space. Similarly, robots used in manufacturing, package/food delivery or search and rescue operations in disaster areas, use AI to sense complex (and sometimes hostile) environments and adapt their responses accordingly. Robots, with ability to recognize faces and human emotions, have also been used in retail environments to direct traffic and enrich the shopping experience.
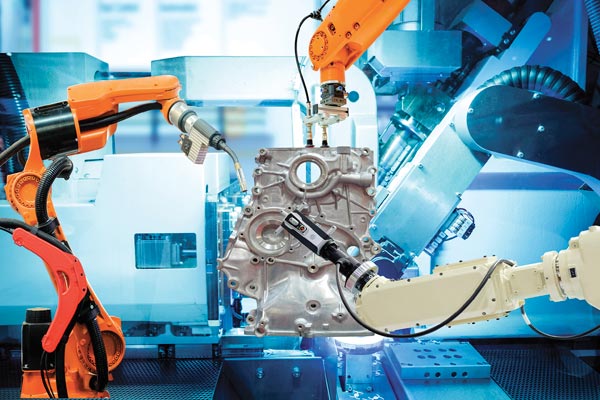
Industrial automation
 Computer vision with AI can be used to improve quality control on the assembly line and help with anomaly detection. AI can also help with predictive maintenance of the machinery to avoid downtime, improve machine life and reduce manufacturing costs. Robots can be used on the manufacturing floor or warehouses to move packages around, assist in the assembly line, inspect product quality and perform repetitive, high precision tasks.
Computer vision with AI can be used to improve quality control on the assembly line and help with anomaly detection. AI can also help with predictive maintenance of the machinery to avoid downtime, improve machine life and reduce manufacturing costs. Robots can be used on the manufacturing floor or warehouses to move packages around, assist in the assembly line, inspect product quality and perform repetitive, high precision tasks.
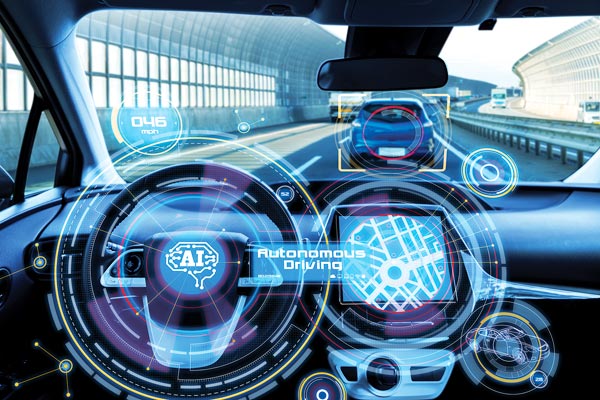
Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous or self-driving vehicles combine IoT and AI to navigate through traffic, respond to changing traffic, weather or road conditions or predict the behavior of pedestrians. AI can also be used to gauge the condition of the vehicle based on collected usage data and provide predictive recommendations for maintenance.
Building/Home automation
AIoT can help companies to reduce their energy costs and make the buildings energy efficient by adjusting lighting and climate control based on building usage and user preference data. Predictive maintenance (using diagnostic data on health of the building systems) allows repairs and maintenance when they are needed rather than on a schedule, thus helping companies save on costs. They can also provide alerts on potential system failures before they happen and help to tune the systems for optimal performance. AI can also be used for automated access control using camera sensors.
Smart Cities
AIoT can open up new ways to create more efficient cities, maintain city infrastructure, and improve public services for communities. This can be done by gathering and analyzing data from multitudes of sensors and IoT devices and extracting actionable insights that can be used to make adjustments in real-time. Practical applications of AI include waste management, public services such as parking management, traffic management and smart lighting. As an example, drones can be used to monitor traffic in real-time and the data can be used to adjust traffic lights or lane assignments in order to manage and reduce traffic jams, all without intervention by humans. Similarly, sensors attached to waste bins can alert the operators to pick up the garbage only when the bins are full, thus helping to reduce costs.
Transportation and Logistics
AI finds application in fleet management by using predictive maintenance, with real-time monitoring of the fleet and proactive maintenance of the vehicles based on data collected from GPS trackers and sensors. AI also helps fleet operators with real-time navigation to reduce fuel costs, tracking vehicle maintenance, and identifying unsafe driver behavior.
AI can help retail in two ways. AI and predictive analytics help to collect and analyze large amounts of data and use that information to help retailers forecast and make accurate, data-driven business decisions. AIoT can use customer intelligence, demographic data and behavioral analytics to provide personalized recommendations to shoppers and improve store operations, product placement strategy, customer service and overall user experience. Retail robots can help to direct traffic and improve the customer experience.
Healthcare
AIoT in healthcare can be used for diverse applications, such as detecting and diagnosing diseases by analyzing imaging data, remote monitoring of patient’s information via sensors and raising alerts when anomalies are seen, predictions of a patient’s risk of diseases by analyzing EHRs (electronic health records) and predicting drug interactions. In addition, robotic surgical systems can perform or assist in very complex and high precision surgeries and make minimally invasive surgery possible.
Renesas and AI
Renesas has a comprehensive family of Arm based MCUs capable of running AI applications. Renesas is working closely with ecosystem partners to bring end-to-end AI solutions in predictive analytics, vision and voice applications, amongst others. Applications using these capabilities span market segments such as industrial automation, smart homes, building automation, healthcare and agriculture.
Renesas’s “e-AI” (embedded AI) solution uses the popular NN models – Caffe developed by UC Berkeley and TensorFlow from Google. It utilizes Deep Neural Network (DNN), a multilayered network that is particularly suited for applications involving image classification, voice recognition or natural language processing. The e-AI tools embedded in the Renesas e2 Studio Integrated Development Environment convert NN models into a form (C/C++ based) that is usable by the MCU and assist in embedding the pre-trained NN model on the target MCU.
AI is the future of IoT
AIoT is enabling new applications and use cases and will help IoT reach its fullest potential. Applications of AIoT can be found in markets as diverse as smart cities, industrial automation, medical, agriculture and smart homes. We will continue to see a rise in new applications that will incorporate AI in IoT end points, and more and more manufacturers will make AIoT an area of significant investment.
About the author
Kavita Char is a Senior Staff Product Marketing Manager at Renesas Electronics America. She has over 20 years of experience in software/applications engineering and product management roles. With extensive experience in IoT applications, MCUs and wireless connectivity, she is now responsible for definition and concept to launch management of next-generation Arm based high performance MCUs and solutions at Renesas.
Renesas Electronics Europe | https://www.renesas.com