Arduino is a platform for embedded systems, based on an open-source hardware/software project, designed for ATMEL AVR microcontrollers (but not limited only for them) that form a part of single printed circuit board with the support for I/O line and a standard program language.
Thus, the Arduino name does not refer to a single, specified device, but to a set of technologies defined by the Arduino group.
Author: MSc Paweł Sióda, TME
A huge and ever-increasing popularity of this platform is the effect of the phenomenon similar to the one that caused the emergence of Apple Macintosh. This computer first offered an unknown until then user-frendliness, which caused an increased attention from people who were not much knowledgeable about operating systems, commends etc. Users just wanted to use the computer, and not to delve into rules of its operation. Currently, this idea of the user-friendliness is represented by smartphones. A similar approach in the segment of built-in systems is represented by Arduino offering users a well-considered module construction of boards with easy to extend functionality (a multilevel structure, a so called “sandwich” is created with the use of, among others, many available extension boards colloquially referred to as shields) and thanks to a well-developed Arduino IDE design environment. Thus, to obtain a working and ready device, it is enough to compile a proper hardware configuration and send a programme to it.
Therefore, Arduino is designed for people who, not having much knowledge about built-in systems, would like to be able to build them to achieve their goals (for example let’s imagine an architect who would like to create a colourful illumination of the facade for the self-designed building with the use of RGB LEDs).
The platform can be used for creating self-supporting devices or can be connected to a host-computer. Importantly, the platform works on Windows, Linux and Macintosh OS X. The program language of Arduino is based on the Wiring project (the application can be developed by defining a network of connections between single constituents) and basically C/C++.
A typical Arduino board includes a microcontroller with digital and analogue I/O lines, the USB, Ethernet or serial (for the connection with the host-computer) interface. The computer is used for programming (a microcontroller on the Arduino board has an bootloader implemented – and this is why no dedicated programmer is required) and for the interaction during operating with Arduino. Since the Arduino platform is fully open, apart from the possibility of purchasing a pre-mounted boards, hardware diagrams for people who want to build their own Arduino at their own are also available.
The overview of ready Arduino kits begins with basic Arduino Uno (A000066).
It was built with the use of a 8-bit ATMEGA328 controller. It comes with resources equal to 32kBs of Flash memory, 2kBs of SRAM data memory and 1kB of non-volatile EEPROM memory. The microcontroller runs at 16MHz (to make it possible a quartz generator was mounted on the board). The board includes 14 I/O lines, 6 of which can be used as PWM outputs (pulse-width modulation). 6 of these 14 lines can work as analogue inputs. What is more, on the board there is a USB socket for connecting the host-computer, an ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming with the use of external programmer) connection and a reset button. A pre-programmed microcontroller ATMEGA16U2 was used as a USB-UART TTL converter (serial interface).
The overview of basic parameters of Arduino boards that are available in the TME offer can be found in the following tables.

Arduino UNO (A000066) ATMEGA328 (16MHz, 32kB Flash, 2kB SRAM, 1kB EEPROM)

Arduino Due (A000062) AT91SAM3X8E (ARM, 84MHz, 512kB Flash, 96kB SRAM)

Arduino Mega 2560 (A000067) ATMEGA2560 (16MHz, 256kB Flash, 8kB SRAM, 4kB EEPROM)
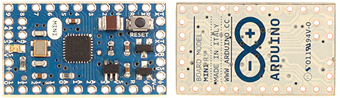
Arduino Mini (A000087) ATMEGA328 (16MHz, 32kB Flash, 2kB SRAM, 512B EEPROM)

Arduino Micro (A000053) ATMEGA32U4 (16MHz, 32kB Flash, 2,5kB SRAM, 1kB EEPROM)
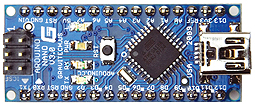
Arduino Nano (A000005) ATMEGA328

Arduino Leonardo (A000057) ATMEGA32U4

Arduino YUN (A000008) ATMEGA32U4

Arduino Esplora (A000095) ATMEGA32U4

Arduino Ethernet (A000068) ATMEGA328
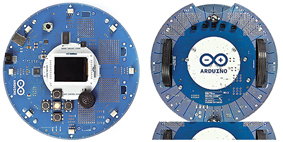
Arduino Robot (A000078) ATMEGA32U4 x2

The offer is complemented with the wide range of extension boards (shield).
The Arduino IDE environment is designed to be an easy tool for hobbyists and people who usually do not have much in common with software design. Obviously, it is fully free and available for download from the Arduino group website (www.arduino.cc). The community of Arduino platform users is huge and fully open; it is extremely easy to find films, instructions, programme codes and complete projects created with its use on the Internet.
www.tme.eu


